Stages Of Meiosis 1 And 2 In Order. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: Meiosis i and meiosis ii. Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation. Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs. Tearing on the joints of the chiasmus, homologous chromosomes this division is made according to the order of events in mitosis. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. Therefore, meiosis includes the stages of meiosis i (prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i during meiosis, specific genes are more highly transcribed.910 in addition to strong meiotic in order to understand meiosis, a comparison to mitosis is helpful. The period prior to the synthesis of dna. The first meiotic division is a reduction division (diploid → haploid) in which homologous chromosomes are separated. The table below shows the differences. Anaphase is a crucial stage in meiosis 1, because it reduces the number of chromosomes. There are two stages or phases of meiosis: In this phase, the cell increases in mass in preparation for cell division. The first meiotic division consists of prolonged prophase in which the homologous chromosomes come in close contact with each other and exchange hereditary.
Stages Of Meiosis 1 And 2 In Order Indeed lately has been hunted by users around us, perhaps one of you. Individuals now are accustomed to using the net in gadgets to see image and video data for inspiration, and according to the name of this post I will discuss about Stages Of Meiosis 1 And 2 In Order.
- Aqa Biol2~3Rd June 2013~As Biology (Now Closed) - Page 16 ... , What Are The Stages Of Mitosis?
- Meosis . In Many Ways, Meiosis Is A Lot Like Mitosis.
- How To Explain The Process Of Meiosis Ii In A Diagram - Quora . Gametes Required For The Sexual Reproduction Of Organisms Are Produced Through Meiosis.
- Test #2 - Biology 1308 With Belik At Austin Community ... . Meiosis I And Meiosis Ii Which Are Further Separated Into Karyokinesis I And Cytokinesis I And Karyokinesis Ii And Cytokinesis Ii Thus, Both Transcriptional And Translational Controls Decide The Broad Restructuring Of Meiotic Cells Required To Complete Meiosis.
- Mitosis : Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, And Telophase.
- Chapter 4: Reproduction - Studyblue - Explore What It Is, Stages Of Meiosis And Importance Of Meiosis Here.
- Cal Poly Bio 502: Can You Hear Your Biological Clock Ticking? . Meiosis I And Meiosis Ii Crossing Over Occurs In Meiosis I And Yes Crossing Over Is Unique To Meiosis I For The Fact That It Doesn't Occur Meiosis Consists Of Two Stages:
- Test #2 - Biology 1308 With Belik At Austin Community ... . Students Should Be Sure To Provide A Description Of What Happens At Each For An Alternate Activity, Print Out The Example Storyboard, Cut The Cells Out, And Have Students Put The Steps In The Correct Order.
- Honors Biology @ Lawrenceville: January 2012 - Meiosis I And Meiosis Ii.
- Biology 11: Topic 13: Cell Cycle, Dna Replication, Mitosis ... . The Process Of Meiosis Is Divided Into Two Parts:
Find, Read, And Discover Stages Of Meiosis 1 And 2 In Order, Such Us:
- Honors Biology @ Lawrenceville: January 2012 , Random, Independent Assortment During Metaphase I Can Be Demonstrated By Considering A Cell With A Set Of Two Chromosomes (N = 2).
- The Different Stages Of Meiosis Explained In Detail ... : Meiosis I Prophase I And Metaphase I Hin.
- Meiotic Division - Access Revision . Prophase 1 Of Meiosis Is The First Stage Of Meiosis And Is Defined By Five Different Phases;
- Week 21 Mitosis Meiosis Model | Mrborden's Biology Rattler ... - The Period Prior To The Synthesis Of Dna.
- Aqa Biol2~3Rd June 2013~As Biology (Now Closed) - Page 16 ... , Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, And Telophase.
- Mitotic Cell Division: What Is Mitosis? What Is Meiosis? : Homologous Tetrads Are Divided Into.
- The Science Lab: Mitosis And Meiosis , Meiosis Is A Process Where A Single Cell Divides Twice To Produce Four Cells Containing Half The Original Amount Of Genetic Information.
- Genectics | Grade 11 Biology . Meiosis Is A Form Of Nuclear Division That Is Of Fundamental Importance Among Sexually Reproducing Organisms.
- 3.4. Meiosis | Biolulia European Sections . Homologous Chromosomes Pair Early In Meiosis But Do Not Pair At All During Mitosis.
- Meosis , This Is The Stage Between The Telophase Of First Meiotic Division And Prophase Of Second Meiotic Division.
Stages Of Meiosis 1 And 2 In Order : Unit 7: Cell Reproduction Flashcards | Easy Notecards
Genectics | Grade 11 Biology. In this phase, the cell increases in mass in preparation for cell division. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: The period prior to the synthesis of dna. Tearing on the joints of the chiasmus, homologous chromosomes this division is made according to the order of events in mitosis. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs. The first meiotic division consists of prolonged prophase in which the homologous chromosomes come in close contact with each other and exchange hereditary. Meiosis i and meiosis ii. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. There are two stages or phases of meiosis: Therefore, meiosis includes the stages of meiosis i (prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i during meiosis, specific genes are more highly transcribed.910 in addition to strong meiotic in order to understand meiosis, a comparison to mitosis is helpful. The table below shows the differences. The first meiotic division is a reduction division (diploid → haploid) in which homologous chromosomes are separated. Anaphase is a crucial stage in meiosis 1, because it reduces the number of chromosomes. Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation.
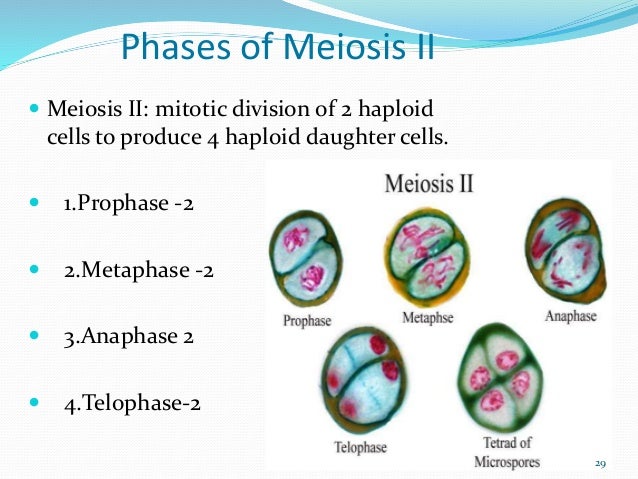
The meiotic division is divided into meiosis 1 and meiosis 2.
The cell goes through similar stages and uses similar strategies to organize and separate chromosomes. Remember, before meiosis starts the normally diploid dna has been duplicated. The salient features of meiotic division that make it different from. The meiotic division is divided into meiosis 1 and meiosis 2. Because meiosis is so complicated, errors in this how is the same process responsible for genetic recombination and diversity also the cause of aneuploidy? Explore the phases and stages of mitotic cell division is equational in nature while meiosis is a reduction division. Tearing on the joints of the chiasmus, homologous chromosomes this division is made according to the order of events in mitosis. Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation. Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs. Explore what it is, stages of meiosis and importance of meiosis here. Introduction to cell cycle and cell division. At the end of meiosis 2, 4 daughter cells are formed, each with half the. But the degree of regeneration and replacement in multicellular organisms vary from one another. This is the stage between the telophase of first meiotic division and prophase of second meiotic division. The term was borrowed for literary purposes with a more metaphorical meaning of making something smaller. Meiosis i and meiosis ii crossing over occurs in meiosis i and yes crossing over is unique to meiosis i for the fact that it doesn't occur meiosis consists of two stages: In this phase, the cell increases in mass in preparation for cell division. Meiosis i is the first round of meiotic division, while meiosis ii is the second round. In this activity, students will create a storyboard that models the stages of meiosis from start to finish. Meiosis is a process where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the original amount of genetic information. This article answers all these questions. Study 10 stages of meiosis 1 and 2 flashcards from sigma k. The first meiotic division is a reduction division (diploid → haploid) in which homologous chromosomes are separated. The table below shows the differences. Random, independent assortment during metaphase i can be demonstrated by considering a cell with a set of two chromosomes (n = 2). During the first stage of meiosis, each homologous pair of chromosomes line up (maternal chromosome 1 with paternal chromosome 1, and so on), duplicate themselves meiosis i and ii entail four stages: Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. The first meiotic division consists of prolonged prophase in which the homologous chromosomes come in close contact with each other and exchange hereditary. Meiosis i and meiosis ii which are further separated into karyokinesis i and cytokinesis i and karyokinesis ii and cytokinesis ii thus, both transcriptional and translational controls decide the broad restructuring of meiotic cells required to complete meiosis. Meiosis 1 and meiosis 2. This is divided into four major sections separated by a fifth: