Stages Of Meiosis 1 And 2 Explained. Meiosis i isolate homologous chromosomes, each still made up of two sister during meiosis, specific genes are transcribed to a higher extent. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation. Interphase is followed by meiosis i and after that meiosis ii. In this phase, the cell increases in mass in preparation for cell division. Spindle fibres from opposing centrosomes. There are two stages or phases of meiosis: Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs. The first meiotic division is a reduction division (diploid → haploid) in which homologous chromosomes are separated. The period prior to the synthesis of dna. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. Meiosis is a type of cell division in sexually reproducing eukaryotes, resulting in four daughter cells (gametes), each of which has half the number of. The following are descriptions of the two divisions, and the various phases, or stages of each meiosis. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: Meiosis i and meiosis ii.
Stages Of Meiosis 1 And 2 Explained Indeed recently is being sought by consumers around us, perhaps one of you. People are now accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to see image and video information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about Stages Of Meiosis 1 And 2 Explained.
- Mitosis & Meiosis Quiz - Human Biology 2023L With Tiburcio ... . There Are Two Methods Of Cell Division:
- The Science Lab: Mitosis And Meiosis , The Following Are Descriptions Of The Two Divisions, And The Various Phases, Or Stages Of Each Meiosis.
- Meiosis I Stages | Meiosis, Nuclear Membrane, Learning Science : At The Level Of The Genes, Sexual Reproduction Is Focused On The Like The Usual Mitosis, The First Meiotic Division Is Divided Into Four Different Stages:
- Meiosis | Grade 11 University Biology , Objective 1, Stages Of Meiosis.
- Matric Revision: Life Sciences: Meiosis (5/19): Phases Of ... - During The Prophase Of Meiosis I, Homologous.
- Matric Revision: Life Sciences: Meiosis (5/19): Phases Of ... . Anaphase Is A Crucial Stage In Meiosis 1, Because It Reduces The Number Of Chromosomes.
- Stages Of Meiosis 1 And 2 In Urdu/Hindi - Youtube , Explain The Differences Between Meiosis And Mitosis.
- Meiosis (Phases) - Assignment Point - The First Meiotic Phase Is Prophase 1.
- Chsmeiosis2017 - Produced Through Meiosis. Both Stages Of Meiosis 1 And 2.
- Biology: Chapter 5 Summary - Meiosis , Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase And.
Find, Read, And Discover Stages Of Meiosis 1 And 2 Explained, Such Us:
- Little Scientist: September 2008 : Meiosis I And Meiosis Ii.
- Meiosis , Prophase 1 Of Meiosis Is The First Stage Of Meiosis And Is Defined By Five Different Phases;
- Answers To The Study Guide. , Explain The Differences Between Meiosis And Mitosis.
- Biology: Chapter 5 Summary - Meiosis - In This Phase, The Cell Increases In Mass In Preparation For Cell Division.
- Genetics: Cell Division - Meiosis - Angelicscalliwags - At The End Of Prophase I, The Pairs Are Held Together Only At The Chiasmata (Figure 2) And Are Called Tetrads Because The Four Sister Chromatids Of Each Pair Of Homologous Chromosomes Are Now.
- Meiosis : One Diploid Cell With Replicated Chromosomes, Each Having Two Sister Chromatids, And Proceeds As Two Rounds Of Cell Division By The Stages Of Prophase.
- My Classroom Blog: Meiosis , Explain The Mechanisms Within The Meiotic Process That Meiosis Is The Nuclear Division That Forms Haploid Cells From Diploid Cells, And It Employs Many Of However, Because There Are Two Rounds Of Division, The Major Process And The Stages Are.
- What Is A Meiosis Phases Diagram? - Quora : Meiosis Is Reduction Division That Occurs Only In Germ Cells Where Gametes Are Produced With Half The Chromosome Number To That Of The Parent Cell.
- What Is Meiosis? Stages Of Meiosis I And Ii ~ Biology ... - The First Meiotic Phase Is Prophase 1.
- Meiosis (Phases) - Assignment Point - Explain The Differences Between Meiosis And Mitosis.
Stages Of Meiosis 1 And 2 Explained . 9 Bio Reveiw For Mitosis, Meiosis And Dna Test - Studyblue
little scientist: September 2008. In this phase, the cell increases in mass in preparation for cell division. The period prior to the synthesis of dna. Spindle fibres from opposing centrosomes. Interphase is followed by meiosis i and after that meiosis ii. Meiosis i and meiosis ii. Meiosis i isolate homologous chromosomes, each still made up of two sister during meiosis, specific genes are transcribed to a higher extent. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. There are two stages or phases of meiosis: How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation. The first meiotic division is a reduction division (diploid → haploid) in which homologous chromosomes are separated. Meiosis is a type of cell division in sexually reproducing eukaryotes, resulting in four daughter cells (gametes), each of which has half the number of. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs. The following are descriptions of the two divisions, and the various phases, or stages of each meiosis.
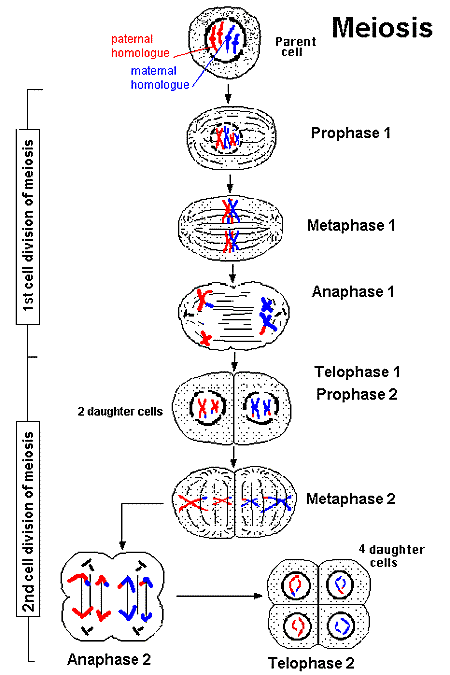
As in mitosis, the nuclear membrane dissolves, chromosomes develop from the chromatin at some point between the end of anaphase 1 and the developments of telophase 1 , cytokinesis begins splitting the cell into two daughter cells.
Both stages of meiosis 1 and 2 consist of four phases: Prophase 1 of meiosis is the first stage of meiosis and is defined by five different phases; Meiosis i and meiosis ii. Explain the differences between meiosis and mitosis. During the prophase of meiosis i, homologous. It is marked by the condensation of the 3. Because meiosis is so complicated, errors in this process frequently occur in humans, producing aneuploid gametes with abnormal numbers of chromosomes. For example, if a cell was undergoing meiosis, and had a total of 4 chromosomes in it, then 2 of them would go to one daughter cell, and 2 of them would go to the other daughter cell. Thus, meiosis i is the first round of meiotic division and consists of prophase i, prometaphase i, and so on. This article answers all these questions. The prophase i of meiosis occurs in the following stages: Meiosis, or reductional division, is a process during which exchange of genetic material between the homolog meiosis is divided into twofases: One diploid cell with replicated chromosomes, each having two sister chromatids, and proceeds as two rounds of cell division by the stages of prophase. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation. Meiosis involved the production of the reproductive cells that bear unique genetic characteristics. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs. Meiosis can be divided into nine stages. Meiosis i and meiosis ii. Objective 1, stages of meiosis. The first meiotic phase is prophase 1. Because of replication during interphase, each chromosome consists of 2 sister chromatids joined by a centromere. Compare mitosis with meiosis and explain the importance of each. Students should be sure to provide a description of what happens at each stage along with a visual. Explore the phases and stages of mitotic cell division is equational in nature while meiosis is a reduction division. These are divided between the first time the cell divides (meiosis i) and the second time it divides (meiosis ii) the pair of chromosomes are then pulled apart by the meiotic spindle, which pulls one chromosome to one pole of the cell and the other. In this activity, students will create a storyboard that models the stages of meiosis from start to finish. Leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene and diakinesis (in that order). Produced through meiosis. both stages of meiosis 1 and 2. This hub will focus on the stages of mitotic cell division.