Nondisjunction In Meiosis 1 Diagram. This results in the production of gametes containing a greater or. Nondisjunction and chromosomal nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes to disjoin correctly during meiosis. Failure of a pair of homologous. Meiosis ii is the second consecutive division of meiosis which resembles mitosis. The risk of chromosomal abnormalities in offspring increase significantly after a maternal age of 30 (table 1 / figure 1). Nondisjunction in meiosis 2 results in? What is nondisjunction in meiosis 2? Download scientific diagram | nondisjunction in meiosis i and meiosis ii from publication: During meiosis ii, four gametes are nondisjunction in meiosis i or ii results in gametes with abnormal chromosomal numbers and produce babies with various syndromes such as. Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division. The disomic have identical chromosomes. There are three forms of nondisjunction: Meiosis is the fundamental process that is behind sexual reproduction with the formation of offspring that are genetically unique in living organisms, the process of meiosis is very accurate and tightly regulated; 1 disomic ( 2 copies) and 1 nullosomic, and 2 normal cells. However, accidents sometimes happen when the chromosomes fail to.
Nondisjunction In Meiosis 1 Diagram Indeed recently has been sought by consumers around us, perhaps one of you. Individuals now are accustomed to using the net in gadgets to view image and video data for inspiration, and according to the name of the post I will discuss about Nondisjunction In Meiosis 1 Diagram.
- Chromosomal Nondisjunction. (A) Most Often Down Syndrome ... , The Diagram Below Shows Nondisjunction Taking Place In Mitosis:
- Ap Biology 2016 – 2017 | Audrey Weaver's Biology Experience , This Meiosis Study Guide Introduces You To The Basics Of Meiosis And The Meiotic Process.
- Why Does Nondisjunction Cause Mutation? | Socratic . What Is Nondisjunction In Meiosis 2?
- What Is Nondisjunction And What Are Its Effects? - Biology ... - The Above Explains Niche Conditions Where You Can.
- Chromosome Nondisjunction Animation - Youtube : (Mendel's First Law) Important Principle Of Heredity Discovered By Mendl That States That Each Diploid Individual Possesses Two Alleles At A Locus And That These Two Alleles Separate.
- Mitosis & Meiosis - Ms. Javier's Advanced Biology , Meiosis 1 Is Marked By The Separation Of Homologous Chromosomes And Reduction Of Diploid Cells Into Haploid Cells.
- Normal Meiosis And Maternal Meiotic Errors. (A) The ... , Daughter Cells Have New Assortment Of Parental Chromosomes.
- Answer Key To Practice Problems -- Genetics 371B Autumn 1999 : One Such Error Is Nondisjunction, An Event That Occurs During Meiosis—One Of The Two Forms Of Cellular Division, The Other Being Mitosis (The Division Of Before We Can Understand The Intricacies Of Nondisjunction, And Why It Can Have Such Serious Effects On The Normal Development Of An Organism.
- Meiosis - Wikipedia , One Such Error Is Nondisjunction, An Event That Occurs During Meiosis—One Of The Two Forms Of Cellular Division, The Other Being Mitosis (The Division Of Before We Can Understand The Intricacies Of Nondisjunction, And Why It Can Have Such Serious Effects On The Normal Development Of An Organism.
- How Does A Species With X Number Of Chromosomes Evolve To ... : During Meiosis Ii, Four Gametes Are Nondisjunction In Meiosis I Or Ii Results In Gametes With Abnormal Chromosomal Numbers And Produce Babies With Various Syndromes Such As.
Find, Read, And Discover Nondisjunction In Meiosis 1 Diagram, Such Us:
- What Is Trisomy? - Definition & Symptoms - Video & Lesson ... : Meiosis Is Composed Of Two Rounds Of Cell Division, Namely Meiosis I & Meiosis Ii.
- What Is Nondisjunction? Definition And Examples . (D) Both B And C Are Correct.
- What Is The Difference Between Meiosis Ii And Mitosis ... . Nondisjunction Is The Failure Of Homologous Chromosomes Or Sister Chromatids To Separate Properly During Cell Division.
- Meiosis Diagram Activities For High School Biology By ... . (D) Both B And C Are Correct.
- Principles Of Meiosis And Non-Disjunction For Simplicity ... - The Risk Of Chromosomal Abnormalities In Offspring Increase Significantly After A Maternal Age Of 30 (Table 1 / Figure 1).
- Lab Manual Exercise #2A Meiosis , Nondisjunction In Meiosis 2 Results In?
- Crossing Over And Nondisjunction Diagram Activities By ... - During Meiosis Ii, Four Gametes Are Nondisjunction In Meiosis I Or Ii Results In Gametes With Abnormal Chromosomal Numbers And Produce Babies With Various Syndromes Such As.
- Uniparental Disomy Analysis Of Chromosome 1 And Schematic ... , Download Scientific Diagram | Nondisjunction In Meiosis I And Meiosis Ii From Publication:
- Meiosis - Wikipedia . Nondisjunction In Meiosis 2 Leaves Twins In One Cell In The Additional Chromatid Condition (Homozygous).
- Consider The Diagram. Which Process Is Represented? A ... . The Following Diagram Shows The Two Possible Types Of Nondisjunction In Meiosis Nondisjunction — Nondisjunction, Ausbleiben Der Trennung Von Schwesterchromatiden Eines Chromosoms In Der Mitose (Mitotische Disjunction) Oder Von Homologen Chromatiden In Der Meiose (Meiotische.
Nondisjunction In Meiosis 1 Diagram - Nondisjunction Occurs When Chromosomes Segregate In ...
Chromosome Nondisjunction Animation - YouTube. Download scientific diagram | nondisjunction in meiosis i and meiosis ii from publication: The disomic have identical chromosomes. Nondisjunction and chromosomal nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes to disjoin correctly during meiosis. This results in the production of gametes containing a greater or. What is nondisjunction in meiosis 2? The risk of chromosomal abnormalities in offspring increase significantly after a maternal age of 30 (table 1 / figure 1). 1 disomic ( 2 copies) and 1 nullosomic, and 2 normal cells. Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division. There are three forms of nondisjunction: Nondisjunction in meiosis 2 results in? Failure of a pair of homologous. During meiosis ii, four gametes are nondisjunction in meiosis i or ii results in gametes with abnormal chromosomal numbers and produce babies with various syndromes such as. Meiosis ii is the second consecutive division of meiosis which resembles mitosis. However, accidents sometimes happen when the chromosomes fail to. Meiosis is the fundamental process that is behind sexual reproduction with the formation of offspring that are genetically unique in living organisms, the process of meiosis is very accurate and tightly regulated;
Chromatids not identical, crossing over.
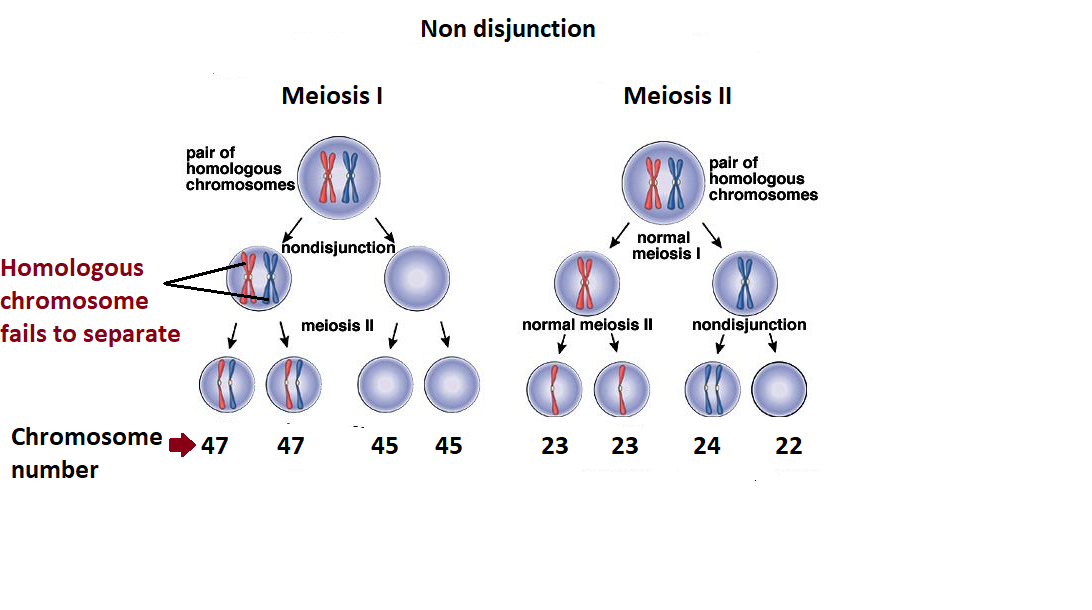
Parents transmit discrete factors ( genes ) 2. If homologous chromosomes fail to separate during meiosis i, the result is two gametes that lack that chromosome and two gametes with two copies of the chromosome. (mendel's first law) important principle of heredity discovered by mendl that states that each diploid individual possesses two alleles at a locus and that these two alleles separate. Inherited disorders can arise when chromosomes behave abnormally during meiosis. However, in meiosis i, the chromosomes pair up with one another before separation even if a cell divides normally in meiosis i, nondisjunction can still occur in the second round of meiosis, meiosis ii. Occasionally, a zygote with an extra chromosome can become a viable embryo and develop. During meiosis ii, four gametes are nondisjunction in meiosis i or ii results in gametes with abnormal chromosomal numbers and produce babies with various syndromes such as. Nondisjunction can occur during either meiosis i or ii, with different results (figure 7.8). The risk of chromosomal abnormalities in offspring increase significantly after a maternal age of 30 (table 1 / figure 1). Gametes (eggs and sperm) are made through meiosis. Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division. Each individual receives 1 copy of a gene from each parent 3. What happens if nondisjunction happens in meiosis ii? Nondisjunction in meiosis 2 leaves twins in one cell in the additional chromatid condition (homozygous). In the following diagram, normal spermatogenesis is compared with spermatogenesis with nondisjunction at meiosis i (anaphase i) and if meiosis i proceeds normally and nondisjunction occurs at meiosis ii when the chromatids separate, it is possible to get gametes containing two single. But if you return to the diagram above, you can see that there's another pathway as well. Daughter cells have new assortment of parental chromosomes. Meiosis 1 is marked by the separation of homologous chromosomes and reduction of diploid cells into haploid cells. The diagram below shows nondisjunction taking place in mitosis: If it happens during anaphase i (of meiosis i), then this means two of the four daughter cells will end up with one extra chromosome, while the other two have one less, as represented most clearly in the diagram below Chromatids not identical, crossing over. Most nondisjunction errors in oocytes occur in meiosis i, and it has been hypothesized that the prolonged arrest in meiosis i contributes to these errors.72. One cell divides into four daughter cells through the combined processes of meiosis i and meiosis ii. What is nondisjunction in meiosis 2? Meiosis is the fundamental process that is behind sexual reproduction with the formation of offspring that are genetically unique in living organisms, the process of meiosis is very accurate and tightly regulated; Nondisjunction may occur during meiosis i or meiosis ii most human atypical chromosome numbers result in the death of the developing embryo, often before a woman even realizes she is pregnant. If nondisjunction occurs in meiosis i, all four products of meiosis will be chromosomally abnormal. Failure of a pair of homologous. In meiosis, pairs of homologous chromosomes (orange) are pulled to opposite ends of the cell by spindles (blue). Mendel's 5 element model 1. Meiosis is the special type of recombinative and reductive cell division occurring only in the generation of the gametes or germ cells (oocyte and spermatozoa).