Meiosis 2N=6 Chromosomes. The first meiotic division is also known as the heterotypic division. When fertilization occurs, two cells with n chromosomes combine. During meiosis, genetic information is exchanged between the maternally and paternally inherited copies of a pair of chromosomes in order to create new combinations of genes. The act of fertilization includes two cells fusing together to become a new zygote. 22 meiosis i separates the homologous chromosome pairs prophase i: Meiosis i consists of the following steps N in this context refers to the number of chromosomes, that is, how many different chromosomes there are in a cell line. Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. In xn (as in 2 n ), x is the number of chromosome sets , and n is the. Because the chromosome number of a species remains the same from one generation to the next, the chromosome number of germ cells must be reduced. If the number of alleles of each gene is not reduced to 1 in the. Chromosomes condense homologous chromosome pair to form a tetrad one member of the pair is from the mom, the other from the dad a tetrad is the association of four chromatids (two from each homologue). This process of genetic recombination helps to increase genetic. Meiosis, from the greek word meioun, meaning to make small, refers to the specialized process by which germ cells divide to produce gametes. The first meiotic division consists of prolonged prophase in which the homologous chromosomes come in close contact with each other and exchange hereditary material between them.
Meiosis 2N=6 Chromosomes Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view image and video data for inspiration, and according to the title of this post I will talk about about Meiosis 2N=6 Chromosomes.
- Chap 6 . Meiosis, From The Greek Word Meioun, Meaning To Make Small, Refers To The Specialized Process By Which Germ Cells Divide To Produce Gametes.
- 13 Lecture Biol 1030-30 Gillette College : Diploid Cells Can Be Represented As 2N.
- Mitosis And Meiosis - Ms. Javier's Biology Course - How Homologous Chromosomes Exchange Fragments In Prophase I.
- Topic 9 Dna Replication, Cell Division, Mitosis & Meiosis ... : This Review Describes The Consequences Of Mitotic And Meiotic Errors Focusing On Novel Concepts And Human Health.
- 2N=6 Mitosis Diagram - Meiosis Is A Specialized Cell Division Required For The Formation Of Gametes (Sperm And Egg).
- Diviziunea Indirecta : Drag One Label Into Each Space At The Right Of The Table.
- 11Photo : How Many Chromosomes Will The Resulting Gametes Have In Each Of The Following Cases?
- Meiosis | Carlson Stock Art . A Nuclear Membrane Forms Around The Chromosomes In Each Of The 4 New Cells.
- Print Bio 142 Chapter 27 Flashcards | Easy Notecards , Homologous Chromosomes Are Two Chromosomes—One Inherited From The Mother, One From The Father—That Have The Same Length And General Appearance.
- Meiosis | Carlson Stock Art . In Xn (As In 2 N ), X Is The Number Of Chromosome Sets , And N Is The.
Find, Read, And Discover Meiosis 2N=6 Chromosomes, Such Us:
- Life Cycles And Meiosis - Biological Sciences 1100 With ... . In Humans, The Diploid Chromosome Number Is 46.
- 2N 6 Meiosis Diagram - Homologous Chromosomes Are Two Chromosomes—One Inherited From The Mother, One From The Father—That Have The Same Length And General Appearance.
- Biology In Focus - Chapter 10 . During Meiosis I Homologous Chromosomes Segregate.
- Cell Division: Mitosis And Meiosis | Biology 1510 ... : How Many Chromosomes Will The Resulting Gametes Have In Each Of The Following Cases?
- 13 Lecture Biol 1030-30 Gillette College . As Meiosis Proceeds Further, Number Of Loops Gradually Decreases And The Loops Ultimately Disappear Due To Disintegration Rather Than Reabsorption Back Into The Chromomere.
- Chap 6 : Drag One Label Into Each Space At The Right Of The Table.
- Dna - What Is A Chromosome? - Biology Stack Exchange . Meiosis Is A Special Type Of Cell Division Necessary For Sexual Reproduction.
- 2N 6 Meiosis Diagram . 22 Meiosis I Separates The Homologous Chromosome Pairs Prophase I:
- Chapter 22 - Drag One Label Into Each Space At The Right Of The Table.
- 13 Meiosis Text . Meiosis I Consists Of The Following Steps
Meiosis 2N=6 Chromosomes , 2N=6 Meiosis Diagram
Solved: Suppose A Diploid Cell With Three Pairs Of Homolog .... This process of genetic recombination helps to increase genetic. Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The first meiotic division is also known as the heterotypic division. Chromosomes condense homologous chromosome pair to form a tetrad one member of the pair is from the mom, the other from the dad a tetrad is the association of four chromatids (two from each homologue). Meiosis i consists of the following steps Because the chromosome number of a species remains the same from one generation to the next, the chromosome number of germ cells must be reduced. N in this context refers to the number of chromosomes, that is, how many different chromosomes there are in a cell line. The first meiotic division consists of prolonged prophase in which the homologous chromosomes come in close contact with each other and exchange hereditary material between them. When fertilization occurs, two cells with n chromosomes combine. The act of fertilization includes two cells fusing together to become a new zygote. In xn (as in 2 n ), x is the number of chromosome sets , and n is the. Meiosis, from the greek word meioun, meaning to make small, refers to the specialized process by which germ cells divide to produce gametes. If the number of alleles of each gene is not reduced to 1 in the. During meiosis, genetic information is exchanged between the maternally and paternally inherited copies of a pair of chromosomes in order to create new combinations of genes. 22 meiosis i separates the homologous chromosome pairs prophase i:
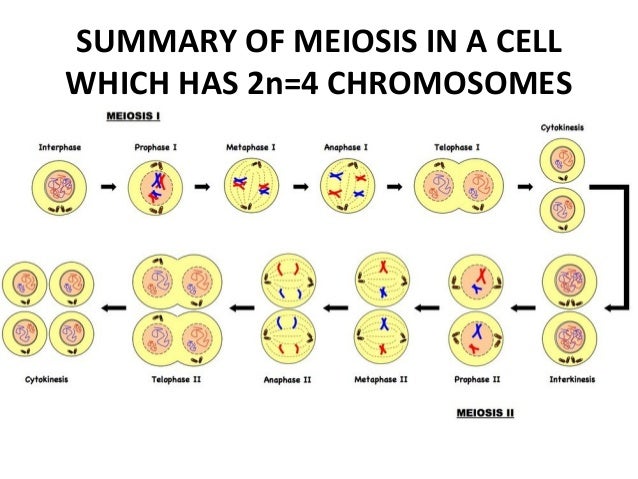
Among plants, chromosome number varies from 2n = 4 in haplopappus gracilis (compositae) to 2n=> 1200 in some pteridophytes.
Lastly, chromosome segregation errors during gamete formation in meiosis are a primary cause of human birth defects and infertility. The first meiotic division consists of prolonged prophase in which the homologous chromosomes come in close contact with each other and exchange hereditary material between them. Meiosis occurs normally (no nondisjunction) 2. Among plants, chromosome number varies from 2n = 4 in haplopappus gracilis (compositae) to 2n=> 1200 in some pteridophytes. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Thus, the karyotype of an organism and its risk of meiotic missegregation influence the shape and evolution of its recombination landscape. How homologous chromosomes exchange fragments in prophase i. This review describes the consequences of mitotic and meiotic errors focusing on novel concepts and human health. Meiosis ii resembles mitosis in that sister chromatids segregate from each other. Lastly, chromosome segregation errors during gamete formation in meiosis are a primary cause of human birth defects and infertility. As meiosis proceeds further, number of loops gradually decreases and the loops ultimately disappear due to disintegration rather than reabsorption back into the chromomere. The act of fertilization includes two cells fusing together to become a new zygote. Meiosis is a specialized cell division required for the formation of gametes (sperm and egg). Of course if an organism has 2. A nuclear membrane forms around the chromosomes in each of the 4 new cells. Meiosis i consists of the following steps This process of genetic recombination helps to increase genetic. Different types of aneuploidy are sometimes represented symbolically; A cell from an organism with a diploid number of 6 (2n=6) is depicted here following chromosome duplication and condensation. Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. When fertilization occurs, two cells with n chromosomes combine. Drag one label into each space at the right of the table. If the number of alleles of each gene is not reduced to 1 in the. In humans, the diploid chromosome number is 46. Meiosis i segregates homologous chromosomes, which are joined as tetrads (2n, 4c), producing two haploid cells (n chromosomes, 23 in humans) which each contain 6.1 chromosomes and meiosis key concept gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. 22 meiosis i separates the homologous chromosome pairs prophase i: Early in meiosis, the chromosome pairs that we inherit from our mother and we mutated the gene that encodes for stag3 in mouse and discovered that it results in meiotic failure and absence of gametes. A form of nuclear division that divides a dipoid cell into haploid? Number of chromosomes nondisjunction event in gametes 1. This feat is performed by a miraculous cellular zipper called the synaptonemal. Meiosis, from the greek word meioun, meaning to make small, refers to the specialized process by which germ cells divide to produce gametes.