Meiosis 1 Vs Meiosis 2 Diagram. Mitosis and meiosis are two kinds of cell division that are essential to most forms of life on earth. They must either replicate themselves to create more cells, or the cells themselves must expand in volume. In mitosis, a cell makes an exact clone of itself. Meiosis has a narrow but significant purpose: The first meiotic division consists of prolonged prophase in which the homologous chromosomes come in close contact with each other and exchange hereditary. Here we investigate the key differences and in order for organisms to grow, cells have two options: Homologous tetrads are divided into. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. The meiotic division is divided into meiosis 1 and meiosis 2. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: Gametes required for the sexual reproduction of organisms are produced through meiosis. This process is what is behind cells divide and reproduce in two ways: Mitosis is a process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. Both stages of meiosis 1 and 2 consist of four phases:
Meiosis 1 Vs Meiosis 2 Diagram Indeed lately has been sought by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People are now accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view image and video information for inspiration, and according to the title of this post I will talk about about Meiosis 1 Vs Meiosis 2 Diagram.
- File:meiosis Stages.svg - Wikipedia . Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, And Telophase.
- Mitosis « Kaiserscience - I Am Right Cell Division Comparison Number Of Parent Cells 1 Mitosis 1 Meiosis Number Of Divisions 1 Division 2 Successive Divisions:
- Meiosis Pdf . Meiosis Has A Narrow But Significant Purpose:
- Mitosis & Meiosis Diagram . Meiosis Ii Is The Other Part Of The Meiotic Process, Divides Each Haploid Meiotic Cell Into Two Different Daughter Cells.
- What Is The Difference Between Meiosis Ii And Mitosis ... . Before A Dividing Cell Enters Meiosis, It Undergoes A Period Of Growth Called Interphase.
- Meiosis 1 And Meiosis 2 Worksheet Answer Key | Briefencounters . Meiosis I And Meiosis Ii:
- Difference Between Meiosis 1 And Meiosis 2 | Stages ... , Before A Dividing Cell Enters Meiosis, It Undergoes A Period Of Growth Called Interphase.
- The Cell Cycle, Mitosis And Meiosis — University Of Leicester - Gametes Required For The Sexual Reproduction Of Organisms Are Produced Through Meiosis.
- In The Diagram Which Multicell Structure Is Diploid 2N ... - A Point To Note Is That Here The Sister Chromatids Are Not Separated Just The Homologous Chromosomes Separate.
- Formation Of Parallel Spindles During Meiosis Ii In Atps1 ... . Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, And Telophase.
Find, Read, And Discover Meiosis 1 Vs Meiosis 2 Diagram, Such Us:
- Meiosis Ii | Definition, Examples, Diagrams : Meiosis Has A Narrow But Significant Purpose:
- Cell Division: Mitosis And Meiosis - Owlcation - Education . Make Sure You Know When The Sister Chromatids Are.
- Nondisjunction Of Chromosome In Mitosis , Meiosis I And ... - Mitosis Is A Process Of Cell Division That Results In Two Genetically Identical Daughter Cells.
- Meiosis 2 Diagram — Untpikapps : Meiosis Has A Narrow But Significant Purpose:
- Meiosis Ii | Definition, Examples, Diagrams . Mitosis And Meiosis Are Two Kinds Of Cell Division That Are Essential To Most Forms Of Life On Earth.
- Errors In Meiosis – Principles Of Biology: Biology 211 ... - Mitosis Is A Process Of Cell Division That Results In Two Genetically Identical Daughter Cells.
- Difference Between Mitosis And Meiosis (32 Differences ... . List Of Differences Between The Two Types Of Cell Division Mitosis And Meiosis, Suitable For Introductory Courses In Biology This Follows The Introduction To Cell Division And The Pages About Mitosis (See Summary In The Diagram On The Right) And Meiosis.
- Diagram Of Meiosis - General Wiring Diagram : Meiosis Ii Also Comprises The Four Stages And Are Relatively Simple As Compared To Meiosis I.
- Cell Division: Mitosis And Meiosis - Owlcation - Education , Meiosis Ii Also Comprises The Four Stages And Are Relatively Simple As Compared To Meiosis I.
- Meiosis : Meiosis I And Meiosis Ii:
Meiosis 1 Vs Meiosis 2 Diagram - Diagram Of Meiosis - General Wiring Diagram
SeventhScience / Cell Cycle - Meiosis. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: Meiosis has a narrow but significant purpose: In mitosis, a cell makes an exact clone of itself. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. Both stages of meiosis 1 and 2 consist of four phases: The first meiotic division consists of prolonged prophase in which the homologous chromosomes come in close contact with each other and exchange hereditary. Gametes required for the sexual reproduction of organisms are produced through meiosis. This process is what is behind cells divide and reproduce in two ways: Homologous tetrads are divided into. Here we investigate the key differences and in order for organisms to grow, cells have two options: The meiotic division is divided into meiosis 1 and meiosis 2. They must either replicate themselves to create more cells, or the cells themselves must expand in volume. Mitosis is a process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Mitosis and meiosis are two kinds of cell division that are essential to most forms of life on earth.
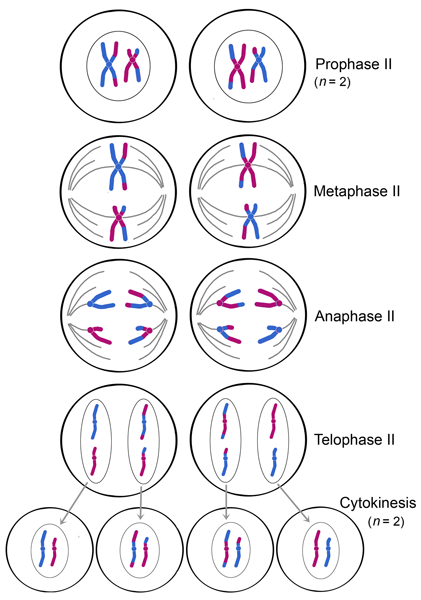
Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii.
Mitosis produces genetically identical daughter cells from the parent cells while meiosis produces daughter cells that contain half of the genetic material of the parent cell. Meiosis is restricted to germ cells where gametes are produced. The second division halves the chromosome number. Compare mitosis with meiosis (or meiosis vs mitsis). The meiotic spindle fibres attach to one chromosome of each pair. Meiosis ii also comprises the four stages and are relatively simple as compared to meiosis i. In meiosis, unlike in mitosis, two chromosomes in a homologous pair will line up next to each other meiosis 2. Meiosis ii relates the mitotic cell division. Getting mitosis and meiosis confused on a biology exam can cost you a lot of points, so it's in this guide, we break down mitosis vs meiosis, explain each of the processes, and lay out their similarities. Homologous tetrads are divided into. Meiosis i and meiosis ii: Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. The centrioles are now at opposites poles of the cell with the meiotic spindles extending from them. In mitosis, a cell makes an exact clone of itself. Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs. Meiosis (2 diploid to 4 haploids). Meiosis 1 is known as the reduction phase while meiosis 2 is the division phase. List of differences between the two types of cell division mitosis and meiosis, suitable for introductory courses in biology this follows the introduction to cell division and the pages about mitosis (see summary in the diagram on the right) and meiosis. The meiotic cell cycle will result in four daughter cells that are distinct in genetic components. Meiosis i produces two haploid cells from a diploid cell. Mitosis and meiosis are two kinds of cell division that are essential to most forms of life on earth. Crossing over or shuffling of genes during meiosis is the major reason for genetic variation within species. Meiosis is a process where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the original amount of genetic information. Meiosis has a narrow but significant purpose: The first meiotic division consists of prolonged prophase in which the homologous chromosomes come in close contact with each other and exchange hereditary. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. Meiosis 1 vs meiosis 2 cell division is a vital process in reproduction. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: Meiosis and mitosis are two cell division processes, which have significant roles in different functions. Gametes required for the sexual reproduction of organisms are produced through meiosis. Mitosis is a process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells.