Meiosis 1 Phases In Order. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. Explore the phases and stages of mitotic cell division is equational in nature while meiosis is a reduction division. Remember, before meiosis starts the normally diploid dna has been duplicated. The first meiotic division consists of prolonged prophase in which the homologous chromosomes come in close contact with each other and exchange hereditary. The following are descriptions of the two divisions, and the various phases, or stages of each meiosis. Prophase 1 of meiosis is the first stage of meiosis and is defined by five different phases; Since cell division occurs twice during meiosis, one starting cell can produce four gametes (eggs or sperm). Meiosis occurs in two distinct divisions, with different phases in each. The cell goes through similar stages and uses similar strategies to organize and separate chromosomes. In each round of division. In this very active phase, the cell synthesizes its vast range of proteins, including the enzymes and structural proteins it will require for development thus, both transcriptional and translational controls decide the broad restructuring of meiotic cells required to complete meiosis. In many ways, meiosis is a lot like mitosis. The salient features of meiotic division that make it different from. Meiosis 1 is marked by the separation of homologous chromosomes and reduction of diploid cells into haploid cells. • growth 1 (g1) phase:
Meiosis 1 Phases In Order Indeed lately is being sought by consumers around us, perhaps one of you. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to see video and image data for inspiration, and according to the title of the post I will talk about about Meiosis 1 Phases In Order.
- Mitotic Cell Division: What Is Mitosis? What Is Meiosis? , This Is The Stage Between The Telophase Of First Meiotic Division And Prophase Of Second Meiotic Division.
- List The 4 Stages Of Mitosis. What Are The Stages Of ... , Spindle Fibres From Opposing Centrosomes.
- Ap Biology For Dummies: Mitosis Vs ... - Meiosis Is Divided Into Twofases:
- Stages Of Meiosis | Firmanbiologi's Blog - Dna Replication Precedes The Start Of Meiosis I.
- Cell Biology - Mitosis Versus Meiosis I: What's The ... : How Are Mitosis And Meiosis Different?
- Biology 11: Topic 13: Cell Cycle, Dna Replication, Mitosis ... . The Following Are Descriptions Of The Two Divisions, And The Various Phases, Or Stages Of Each Meiosis.
- Cheo Licensed For Non-Commercial Use Only / Mitosis And ... . Again, Chromosomes Condense, The Nuclear Envelop Breaks Down, And The Spindle Apparatus Forms.
- Meiosis Chart - At The End Of The Meiotic Process, Four Daughter Cells Are Produced.
- Mitosis Meiosis - Meiosis I And Meiosis Ii.
- Meiosis Models Set : During Meiosis, Genetic Information Is Exchanged Between The Maternally And Paternally Inherited Copies Of A Pair Of Chromosomes In Order To Create New Combinations Of Genes.
Find, Read, And Discover Meiosis 1 Phases In Order, Such Us:
- The Cell Cycle, Mitosis And Meiosis — University Of Leicester : Meiosis Occurs In Two Distinct Divisions, With Different Phases In Each.
- What Is A Meiosis Phases Diagram? - Quora , The First Meiotic Division Is A Reduction Division (Diploid → Haploid) In Which Homologous Chromosomes Are Separated.
- Meiosis And Sexual Reproduction - Explore The Phases And Stages Of Mitotic Cell Division Is Equational In Nature While Meiosis Is A Reduction Division.
- Chromosome Replication | Mariko's Blog , Leptotene, Zygotene, Pachytene, Diplotene And Diakinesis (In That Order).
- Mitotic Cell Division: What Is Mitosis? What Is Meiosis? , Meiosis Is Preceded By An Interphase Which Is Nearly Identical To The Interphase Preceding Mitosis.
- Chromosome Replication | Mariko's Blog , The Centrosomes, Which Are The Structures That Organize The Microtubules Of The Meiotic.
- Chromosome Replication | Mariko's Blog : The Purpose Of Meiosis 1 Is To Separate Homologous Chromosomes, Whereas The Purpose Of Meiosis Ii Is To Separate Previously Viewed.
- The Process Of Meiosis | Biology I : In This Very Active Phase, The Cell Synthesizes Its Vast Range Of Proteins, Including The Enzymes And Structural Proteins It Will Require For Development Thus, Both Transcriptional And Translational Controls Decide The Broad Restructuring Of Meiotic Cells Required To Complete Meiosis.
- What Is Mitosis? | Mitosis, Teaching Biology, Daughter Cells - Introduction To Eukaryotic Cell Cycles.
- Meiosis Model - 1013869 - 3B Scientific - R02/1 - Biology ... : In Each Round Of Division.
Meiosis 1 Phases In Order : Final Bio Exam -- Mitosis And Meiosis - Art And Art ...
Meiosis I Stages | Meiosis, Nuclear membrane, Learning science. • growth 1 (g1) phase: Since cell division occurs twice during meiosis, one starting cell can produce four gametes (eggs or sperm). In this very active phase, the cell synthesizes its vast range of proteins, including the enzymes and structural proteins it will require for development thus, both transcriptional and translational controls decide the broad restructuring of meiotic cells required to complete meiosis. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. Prophase 1 of meiosis is the first stage of meiosis and is defined by five different phases; Meiosis occurs in two distinct divisions, with different phases in each. In many ways, meiosis is a lot like mitosis. The cell goes through similar stages and uses similar strategies to organize and separate chromosomes. Remember, before meiosis starts the normally diploid dna has been duplicated. The salient features of meiotic division that make it different from. Meiosis 1 is marked by the separation of homologous chromosomes and reduction of diploid cells into haploid cells. Explore the phases and stages of mitotic cell division is equational in nature while meiosis is a reduction division. The first meiotic division consists of prolonged prophase in which the homologous chromosomes come in close contact with each other and exchange hereditary. The following are descriptions of the two divisions, and the various phases, or stages of each meiosis. In each round of division.
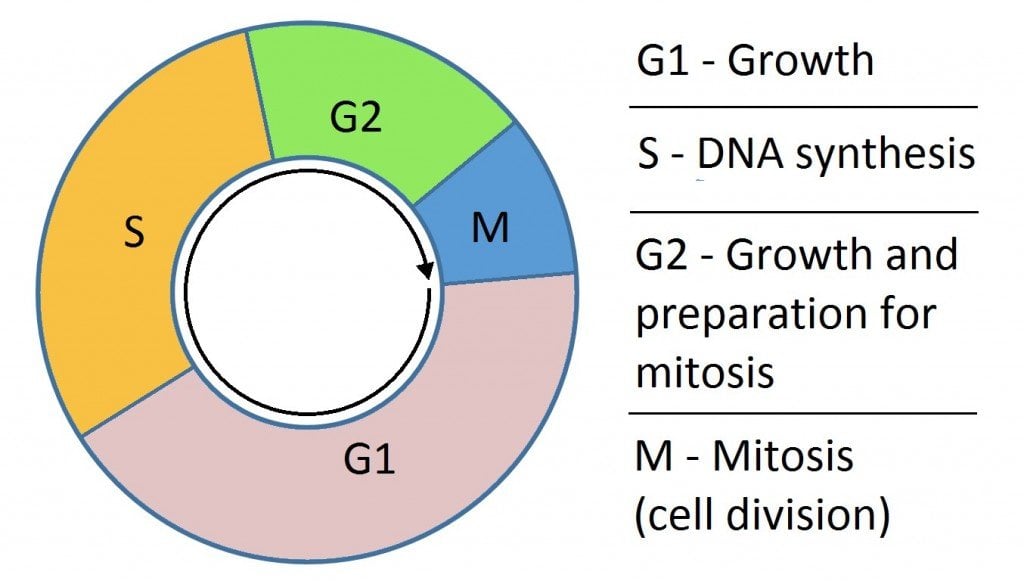
Meiosis is preceded by an interphase which is nearly identical to the interphase preceding mitosis.
Meiosis i and meiosis ii. In many ways, meiosis is a lot like mitosis. Litotes refers to the practice of negating something in order to prove the opposite. In this video paul andersen explains the major phases of meiosis including: Meiosis is also known as reductional cell division because four daughter cells produced contain half the number of chromosomes than that of their parent cell. Again, chromosomes condense, the nuclear envelop breaks down, and the spindle apparatus forms. Before mitosis or meiosis i dna is replicated in order to provide the two daughter cells in meiosis i with chromosomes from the parent cell. During interphase, the dna of the chromosomes is cohesin holds the chromatids together until anaphase ii. Remember, before meiosis starts the normally diploid dna has been duplicated. Introduction to eukaryotic cell cycles. Dna replication precedes the start of meiosis i. The result of meiosis is ultimately 4 cells but not by 1 division. The ordered steps of meiosis ii. Meiosis is a cell division in which four haploid cells are formed from a single diploid cell. Explore the phases and stages of mitotic cell division is equational in nature while meiosis is a reduction division. The centrosomes, which are the structures that organize the microtubules of the meiotic spindle, also. During meiosis, genetic information is exchanged between the maternally and paternally inherited copies of a pair of chromosomes in order to create new combinations of genes. Interphase, prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i, telophase i, cytokinesis. The first meiotic division is a reduction division (diploid → haploid) in which homologous chromosomes are separated. Explore what occurs in each phase of this cell division process. The purpose of meiosis 1 is to separate homologous chromosomes, whereas the purpose of meiosis ii is to separate previously viewed. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase which is nearly identical to the interphase preceding mitosis. Prophase 1 of meiosis is the first stage of meiosis and is defined by five different phases; Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs. In this very active phase, the cell synthesizes its vast range of proteins, including the enzymes and structural proteins it will require for development thus, both transcriptional and translational controls decide the broad restructuring of meiotic cells required to complete meiosis. During prophase i, homologous chromosomes pair and form synapses, a step unique to meiosis. When diploid germ cells divide to produce haploid gametes (sex cells) the process is referred to as meiosis. The cell goes through similar stages and uses similar strategies to organize and separate chromosomes. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the g1, s, and g2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. Cohesin holds the chromatids together until anaphase ii. In meiosis i, chromosomes in a diploid cell resegregate, producing four haploid daughter cells.