Meiosis 1 And 2 Nondisjunction. If it happens during anaphase i (of meiosis i), then one pair of homologous chromosomes remains unseparated. This means two of the four daughter cells will end up with one extra chromosome, while the other two have. The process of meiosis is essential for all sexually reproducing organisms for the following reasons: The disomic have identical chromosomes. The meiosis maintains a constant number of. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division. Nondisjunction in meiosis 1 results in? Nondisjunction in meiosis 2 results in? 1 disomic ( 2 copies) and 1 nullosomic, and 2 normal cells. Failure of a pair of homologous. Nondisjunction can occur during meiosis i and meiosis ii, resulting in abnormal chromosomes number of gametes. The key difference between nondisjunction in meiosis 1 and 2 is that during meiosis 1, homologous chromosomes fail to separate while in meiosis ii sister chromatids fail to. There are three forms of nondisjunction: Chromosomal crossover in meiosis i.
Meiosis 1 And 2 Nondisjunction Indeed lately has been sought by consumers around us, perhaps one of you. Individuals are now accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image data for inspiration, and according to the title of the post I will discuss about Meiosis 1 And 2 Nondisjunction.
- Nondisjunction (Genetics) , Postzygotic Nondisjunction, A Failure Of Mitotic Chromatid Separation In The Early Zygote, Causes Similar.
- Unit 3 Meiosis , Prophase Ii, Metaphase Ii, Anaphase Ii, Telophase Ii.
- What Is Meiosis? | Dna Encyclopedia , Only Four Cases Prenatally Diagnosed Were Described Until Now.
- Nondisjunction (Genetics) - Single Nondisjunction In Meiosis 1?
- 2013 Hn Problems In Meiosis 01 Nondisjunction - Youtube . In Biology, Meiosis Is The Process By Which The Number Of Chromosomes In A Cell Nucleus Is Halved During The Formation Of Germ Cells (Eggs And Sperm).
- Non-Disjunction And Down Syndrome (2016) Ib Biology - Youtube - How Can We Know Whether The Rather, It Now Becomes Aacc After Meiosis I.
- Nondisjunction In Meiosis I And Meiosis Ii | Download ... - Meiosis Is The Special Type Of Recombinative And Reductive Cell Division Occurring Only In The Generation Of The Gametes Or Germ Cells (Oocyte And Spermatozoa).
- 9.4.5 Mutations And Nondisjunction - Youtube - Postzygotic Nondisjunction, A Failure Of Mitotic Chromatid Separation In The Early Zygote, Causes Similar.
- Meiosis | Grade 11 University Biology . We Know That Most Trisomies Or Monosomies Occur Due To Nondisjunction In Either Meisosis I Or Meisois Ii.
- What Is Nondisjunction? Definition And Examples , This Means Two Of The Four Daughter Cells Will End Up With One Extra Chromosome, While The Other Two Have.
Find, Read, And Discover Meiosis 1 And 2 Nondisjunction, Such Us:
- 2011 Group Project 3 - Embryology , Only Four Cases Prenatally Diagnosed Were Described Until Now.
- Meiosis And Nondisjunction On Emaze - Failure Of A Pair Of Homologous.
- File:nondisjunction Of Homologous Chromosomes In Meiosis1 ... - Random Combination Of The Gametes 7.
- Meiotic Nondisjunction. Causes, Symptoms, Treatment ... : Therefore, Accurate Segregation Of Homologous Chromosomes During The First Meiotic Division Requires That Recombinant Chromosomes Remain Associated For Decades.
- Nondisjunction In Meiosis: Definition & Examples - Video ... - If Nondisjunction Occurs In Meiosis I, All Four Products Of Meiosis Will Be Chromosomally Abnormal.
- Index Of /Locked/Media/Ch15 . Nondisjunction Is The Failure Of Homologous Chromosomes Or Sister Chromatids To Separate Properly During Cell Division.
- Role Of Nondisjunction | Klinefelter's Syndrome . Nondisjunction In Meiosis 2 Results In?
- Nondisjunction - Definition, Types And Examples | Biology ... - The Resulting Cells Are Haploid;
- 2011 Group Project 3 - Embryology . Let's Say We Have Nondisjunction In.
- Mutation Effects - Fertility Advisors : Chromosome Combinations During Meiosis 8.
Meiosis 1 And 2 Nondisjunction : (Pdf) Nondisjunction And Chromosomal Anomalies
Solved: QUESTION 15 Nondisjunction Is The Failure Of Homol .... Nondisjunction in meiosis 1 results in? There are three forms of nondisjunction: This means two of the four daughter cells will end up with one extra chromosome, while the other two have. 1 disomic ( 2 copies) and 1 nullosomic, and 2 normal cells. The key difference between nondisjunction in meiosis 1 and 2 is that during meiosis 1, homologous chromosomes fail to separate while in meiosis ii sister chromatids fail to. Nondisjunction in meiosis 2 results in? The disomic have identical chromosomes. Nondisjunction can occur during meiosis i and meiosis ii, resulting in abnormal chromosomes number of gametes. The process of meiosis is essential for all sexually reproducing organisms for the following reasons: Chromosomal crossover in meiosis i. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. If it happens during anaphase i (of meiosis i), then one pair of homologous chromosomes remains unseparated. Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division. Failure of a pair of homologous. The meiosis maintains a constant number of.
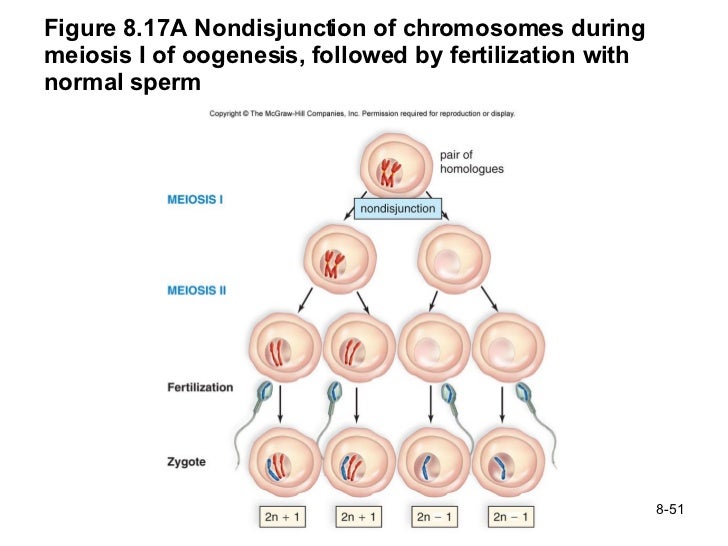
Chromosomal crossover in meiosis i.
Because gametes need to have half the number of chromosomes as normal cells, cells divide twice in meiotic reproduction, which is known as meiosis i and meiosis ii. Nondisjunction can take place in either meiosis i or meiosis ii. Only four cases prenatally diagnosed were described until now. Nondisjunction can occur during either meiosis i or ii, with different results (figure 2). The key difference between nondisjunction in meiosis 1 and 2 is that during meiosis 1, homologous chromosomes fail to separate while in meiosis ii sister chromatids fail to. 1 disomic ( 2 copies) and 1 nullosomic, and 2 normal cells. Postzygotic nondisjunction, a failure of mitotic chromatid separation in the early zygote, causes similar. This could arise from a failure of homologous chromosomes to separate in meiosis i, or the failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis ii or mitosis. Prophase ii, metaphase ii, anaphase ii, telophase ii. The process of meiosis is essential for all sexually reproducing organisms for the following reasons: This means two of the four daughter cells will end up with one extra chromosome, while the other two have. Let's say we have nondisjunction in. If homologous chromosomes fail to separate during meiosis i, the result is two gametes that lack that chromosome and two gametes with two copies of the chromosome. Meiosis i a b meiosis ii b a 1st polar body 24 aa and ab no chr 21! How sister chromatids separate to form gametes. Pentasomy x is a rare chromosomal abnormality probably due to a nondisjunction during the meiosis. The cell at e is n + 1, and resulted from a nondisjunction that occurred during meiosis i (between cell a and cell b.) Nondisjunction can occur during meiosis i and meiosis ii, resulting in abnormal chromosomes number of gametes. Because meiosis is so complicated, errors in this process frequently occur in humans, producing aneuploid gametes with abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Meiosis is all about coming together, and then separating. In biology, meiosis is the process by which the number of chromosomes in a cell nucleus is halved during the formation of germ cells (eggs and sperm). Gamete 22 2nd polar body. Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division. Nondisjunction in meiosis 2 results in? Chromosome combinations during meiosis 8. The resulting cells are haploid; Details of 1st and 2nd divisions of meiosis 5 6. How can we know whether the rather, it now becomes aacc after meiosis i. If it happens during anaphase i (of meiosis i), then one pair of homologous chromosomes remains unseparated. Nondisjunction in meiosis 1 vs 2 | studyblue. Very few aneuploid fetuses survive, and those that do have a high incidence of mental retardation.