Crossing Over Meiosis Simple Diagram. Crossing over and the random orientation of homologue pairs during metaphase of meiosis i. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. Share a brief animation, meiosis: Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs. As an example, consider the meiosis ii diagram above, which shows the end products of meiosis for a simple cell with a diploid number of 2n = 4 this diversity of possible gametes reflects two factors: I use this powerpoint in my biology class at beverly hills high school. Diagram of the meiotic phases. Be prepared to stop the video clip at different points to ask questions: The synaptonemal complex helps to stabilize the pairing of homologous chromosomes and to facilitate recombination or crossing over. Yes, normally occurs between each pair of homologous chromosomes. Over simplification, but in a similar place on each of these it might code for eye color or i don't know, personality. But the synthesis of new chromosome material, at least the dna, occurs during the interphase and thus the gene duplication takes place before the prophase of first meiosis begins. The following points highlight the four theories proposed for the mechanism of crossing over. Nothing is that simple in how tall you get and it's not that simple in dna but just to give you an idea of how it is. The first meiotic division is a reduction division (diploid → haploid) in which homologous chromosomes are separated.
Crossing Over Meiosis Simple Diagram Indeed recently is being sought by users around us, perhaps one of you. People now are accustomed to using the net in gadgets to see image and video data for inspiration, and according to the title of this post I will discuss about Crossing Over Meiosis Simple Diagram.
- Meiosis - Wikipedia , Cell Undergoes Mitosis, And Then Undergoes Pmat Again.
- Meiosis Vs. Mitosis: Comparison | Schoolworkhelper , Crossing Over Is Discussed Later On This Page.
- Meiosis - Be Prepared To Stop The Video Clip At Different Points To Ask Questions:
- Crossing Over Meiosis Diagram | World Of Reference , Meiosis Can Be Divided Into Nine Stages.
- Meiosis - Revision Cards In A Level And Ib Biology - The First Meiotic Division Is A Reduction Division (Diploid → Haploid) In Which Homologous Chromosomes Are Separated.
- Genetic Variation Due To Meiosis : During This Meiotic Process Her 16 Pairs Of Homologous.
- How To Explain The Process Of Meiosis Ii In A Diagram - Quora . Crossing Over Crossing Over, Or Recombination, Is The Exchange Of Chromosome Segments Between Nonsister Chromatids In Meiosis.
- 01 Cell Division: Mitosis And Meiosis | Biology 1510 ... : Meiosis And Crossing Over 8.12Chromosomes Are Matched In Homologous Pairs All Body Cells Except Gametes (Eggs And Sperm) Are Referred To As Somatic Cells, And In Humans Have 46 Chromosomes.
- What Is Meiosis? - Expii . A Determined The Gender B And D Is Part Of Mitosis Not Meiosis.
- What Are Tetrads? Are They Formed In Mitosis? | Socratic . Crossing Over Is Discussed Later On This Page.
Find, Read, And Discover Crossing Over Meiosis Simple Diagram, Such Us:
- Meiosis Notes . This Is The Stage Where Genetic Recombination May Occur (Via Crossing Over).
- Hillis2E_Ch08 . Meiosis Is A Special Type Of Cell Division.
- Meiosis - Revision Cards In A Level And Ib Biology : Crossing Over Is A Biological Occurrence That Happens During Meiosis When The Paired Homologs, Or Chromosomes Of The Same Type, Are Lined Up.
- Test 3 (Ch.10-16) - Biology 1406 With Lai At Austin ... : If The Unfertilized Eggs Develop From Mitotic Oögenesis (Without The Reduction Division Of Normal Meiosis), Then The Diploid Queen Bee Undergoes Normal Meiosis (Oögenesis) Producing Haploid Eggs.
- Phases Of Meiosis And Action In Each Phase Crossing Over ... . Chromosomes Condense, Nuclear Membrane Dissolves, Homologous Chromosomes Form Bivalents, Crossing Over Occurs.
- Chromosome Segregation During Mitosis And Meiosis. (A ... - End Result Is 4 Daughter Cells, Instead Of The Two That Come With Mitosis.
- What Is 'Crossing Over' In Terms Of Biology? - Quora : Over Simplification, But In A Similar Place On Each Of These It Might Code For Eye Color Or I Don't Know, Personality.
- Prophase Ii | Biology Dictionary : Meiosis And Crossing Over 8.12Chromosomes Are Matched In Homologous Pairs All Body Cells Except Gametes (Eggs And Sperm) Are Referred To As Somatic Cells, And In Humans Have 46 Chromosomes.
- Meiosis , These Are Divided Between The First Time The Cell Divides (Meiosis I) And The Second Time It Divides (Meiosis Ii) The Meiotic Spindle, Consisting Of Microtubules And Other Proteins, Extends Across The Cell Between The Centrioles.
- Biology Matters: Cell Division Tutorial Q15B , The Synaptonemal Complex Is Complete, Allowing Chiasma To Form.
Crossing Over Meiosis Simple Diagram - What Happens In Metaphase 1 In Meiosis? Are The Number Of ...
How to explain the process of meiosis II in a diagram - Quora. Diagram of the meiotic phases. Crossing over and the random orientation of homologue pairs during metaphase of meiosis i. Over simplification, but in a similar place on each of these it might code for eye color or i don't know, personality. Share a brief animation, meiosis: As an example, consider the meiosis ii diagram above, which shows the end products of meiosis for a simple cell with a diploid number of 2n = 4 this diversity of possible gametes reflects two factors: Nothing is that simple in how tall you get and it's not that simple in dna but just to give you an idea of how it is. Yes, normally occurs between each pair of homologous chromosomes. The first meiotic division is a reduction division (diploid → haploid) in which homologous chromosomes are separated. The synaptonemal complex helps to stabilize the pairing of homologous chromosomes and to facilitate recombination or crossing over. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. Be prepared to stop the video clip at different points to ask questions: I use this powerpoint in my biology class at beverly hills high school. But the synthesis of new chromosome material, at least the dna, occurs during the interphase and thus the gene duplication takes place before the prophase of first meiosis begins. Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs. The following points highlight the four theories proposed for the mechanism of crossing over.
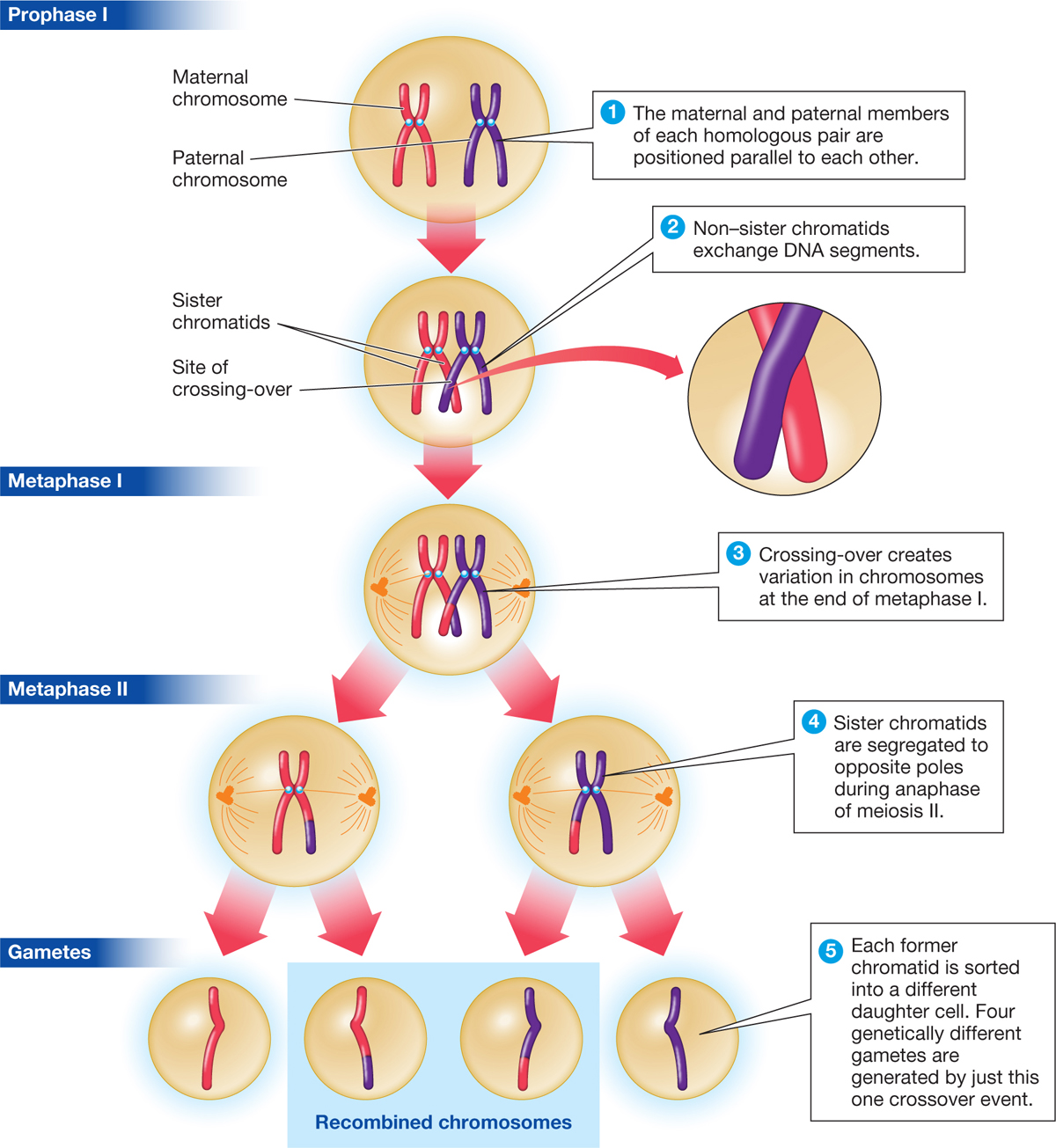
These are divided between the first time the cell divides (meiosis i) and the second time it divides (meiosis ii) the meiotic spindle, consisting of microtubules and other proteins, extends across the cell between the centrioles.
But the synthesis of new chromosome material, at least the dna, occurs during the interphase and thus the gene duplication takes place before the prophase of first meiosis begins. End result is 4 daughter cells, instead of the two that come with mitosis. Share a brief animation, meiosis: Crossing over crossing over, or recombination, is the exchange of chromosome segments between nonsister chromatids in meiosis. These are divided between the first time the cell divides (meiosis i) and the second time it divides (meiosis ii) the meiotic spindle, consisting of microtubules and other proteins, extends across the cell between the centrioles. Crossing over creates new combinations of genes in the gametes that are not found in either parent, contributing to genetic diversity. During meiosis in humans, 1 diploid cell (with 46 chromosomes or 23 pairs) undergoes 2 cycles of cell division but only 1 round of dna replication. Meiotic cell division emphasizing chromosome movement. In simple terms, the crossing over definition equates to genetic recombination. In meiosis, they're lined up on the meiotic plates, as they're sometimes called, and those paired chromosomes then have to have some biological. Each chromosome has a twin with centromere in same position, same length, same. At the start of mitosis, the cpc localises all over the chromosomes and acts to modify chromatin, during. Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs. The synaptonemal complex helps to stabilize the pairing of homologous chromosomes and to facilitate recombination or crossing over. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. It is an equational division through which identical daughter cells are produced having the same amount and type of genetic. Crossing over is discussed later on this page. Meiosis, mechanism of crossover, significance in evolution. Explain that students will need to refer to this diagram during the modeling of crossing over during the independent practice that will follow. Over simplification, but in a similar place on each of these it might code for eye color or i don't know, personality. Cell undergoes mitosis, and then undergoes pmat again. For that reason, meiosis is often called reduction division. Diagram of the meiotic phases. Crossing over occurs during both mitosis and meiosis, though the frequency is much higher in meiosis, according to science gateway. Crossing over or shuffling of genes during meiosis is the major reason for genetic variation within species. The first meiotic division is a reduction division (diploid → haploid) in which homologous chromosomes are separated. The synaptonemal complex is complete, allowing chiasma to form. Four haploid cells figure 6. There is no crossing over in mitosis. Meiosis is a special type of cell division. Meiosis has various timescales in different organisms, which can be affected by several factors mitotic prophase is much shorter that meiotic prophase i.